Have the shadows of leaked videos and online privacy violations truly eclipsed the ethical boundaries of our digital age? The proliferation of "MMS scandals" in India serves as a chilling testament to the vulnerabilities inherent in a hyper-connected world, demanding immediate and sustained attention.
The echoes of these digital breaches reverberate far beyond the initial shockwaves. The dissemination of private, often intimate, content without consent underscores a dangerous disregard for individual rights and the potential for irreversible damage. The grainy quality of the videos, the clunky technology of the era, and the seemingly innocuous nature of multimedia messaging services (MMS) the only conduits for sharing such content at the time belie the profound impact these scandals have had on countless lives.
Consider the case of the DPS MMS scandal, a particularly jarring example. In 2004, a video depicting a class XI couple surfaced on the internet, quickly becoming a national talking point. The 2 minutes and 37 seconds long clip, rapidly circulated and widely viewed, forever altered the lives of those involved and exposed the vulnerability of individuals, particularly young people, to the malicious exploitation of technology.
The Indian legal system, recognizing the urgency of the situation, has established a firm stance against the invasion of privacy and the unauthorized recording and distribution of intimate content. The primary legislation governing these matters is the Information Technology Act, 2000, later amended in 2008 to address the evolving nature of cybercrime and data privacy concerns. This legislation serves as the cornerstone of efforts to prosecute offenders and protect victims of such scandals. However, the legal framework, while essential, is merely one piece of a complex puzzle.
The issue of Indian viral MMS scandals is a multifaceted problem that requires a collective effort from various stakeholders. Legal and technological interventions are vital, but societal awareness and cultural shifts are equally critical to address this issue effectively. A comprehensive approach must address the underlying causes of such incidents, prevent their occurrence, and mitigate their devastating effects.
To understand the scope of the problem, let us delve into the core of the legal framework:
Key Legal Aspects
- The Information Technology Act, 2000 and Amendments: The cornerstone of legal recourse. This Act, amended in 2008, specifically addresses cybercrimes, including the unauthorized dissemination of private information.
- Sections 66E and 67 of the IT Act: Crucial sections that penalize the violation of privacy and the transmission or publication of obscene content.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC): Sections of the IPC, such as those related to voyeurism and stalking, may also be applicable in cases involving MMS scandals.
- Cyber Crime Cells: The crucial role of specialized law enforcement units in investigating and prosecuting such cases.
- Data Protection Bills: The importance of enacting comprehensive data protection laws that offer greater safeguards for personal information.
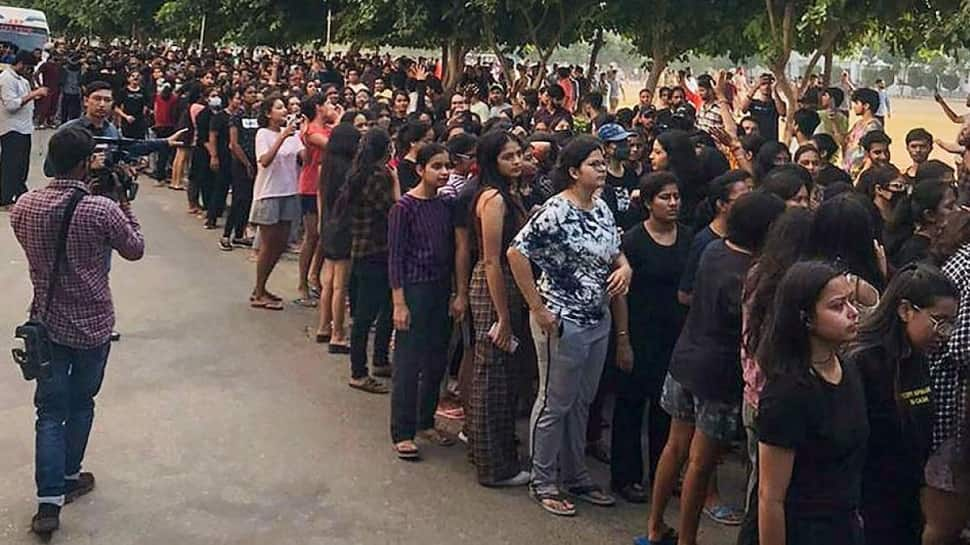
The recent events at Chandigarh University, where students protested against the alleged leak of objectionable videos, are a stark reminder of the continuing relevance and urgency of these issues. The university protests highlighted not just the technical aspects of the leaks but also the profound emotional and psychological impact on the affected students and the wider community. The demand for immediate action underscores the lack of trust in the institutions meant to protect them.
The cases mentioned above are not isolated incidents. They are symptoms of a deeper malaise, a consequence of the rapid evolution of technology outpacing our understanding of its social and ethical implications. The ability to record, share, and disseminate intimate content, coupled with the anonymity afforded by the internet, has created a breeding ground for exploitation and abuse.
The challenges extend beyond the legal domain and require a multi-pronged strategy. This should include:
- Strengthening Law Enforcement: Equipping law enforcement agencies with the necessary resources, training, and expertise to effectively investigate and prosecute cases related to MMS scandals.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Promoting cybersecurity awareness among the general public, particularly young people, to educate them about online safety and the risks associated with sharing personal information.
- Data Privacy: Enforcing stringent data privacy regulations to protect sensitive personal information and prevent unauthorized access and dissemination.
- Mental Health Support: Providing comprehensive mental health support and counseling services to victims of MMS scandals to help them cope with the trauma and emotional distress they experience.
- Media Literacy: Promoting media literacy to help individuals critically evaluate online content, identify misinformation, and understand the ethical implications of sharing and viewing intimate content.
- Parental Guidance: Educating parents on the digital dangers and the significance of their children's online activities.
- Platform Accountability: Holding social media platforms accountable for the content hosted and disseminated on their platforms and requiring them to remove illegal content promptly.
The legal landscape is essential but insufficient on its own. The responsibility extends to parents, educators, and the wider community. Parents must engage with their children about the responsible use of technology, the dangers of online exploitation, and the importance of safeguarding their privacy. Educators have a crucial role to play in promoting digital citizenship and media literacy in schools. The media must report responsibly on such incidents, avoiding sensationalism and focusing on the impact on victims.
The fight against MMS scandals is not a battle that can be won quickly. It requires a sustained commitment from all stakeholders, a willingness to adapt to the ever-changing digital landscape, and a shared recognition of the human cost of these violations. It demands that we confront not just the technological and legal aspects of these issues but also the underlying social and cultural factors that contribute to them.
The future of online privacy in India hinges on our collective response. It requires a commitment to safeguarding individual rights, promoting ethical behavior, and fostering a digital environment where privacy is respected, and vulnerabilities are addressed. Only then can we hope to mitigate the damage caused by these scandals and protect future generations from their devastating consequences. The time to act is now, for the sake of our society, and the people within it.