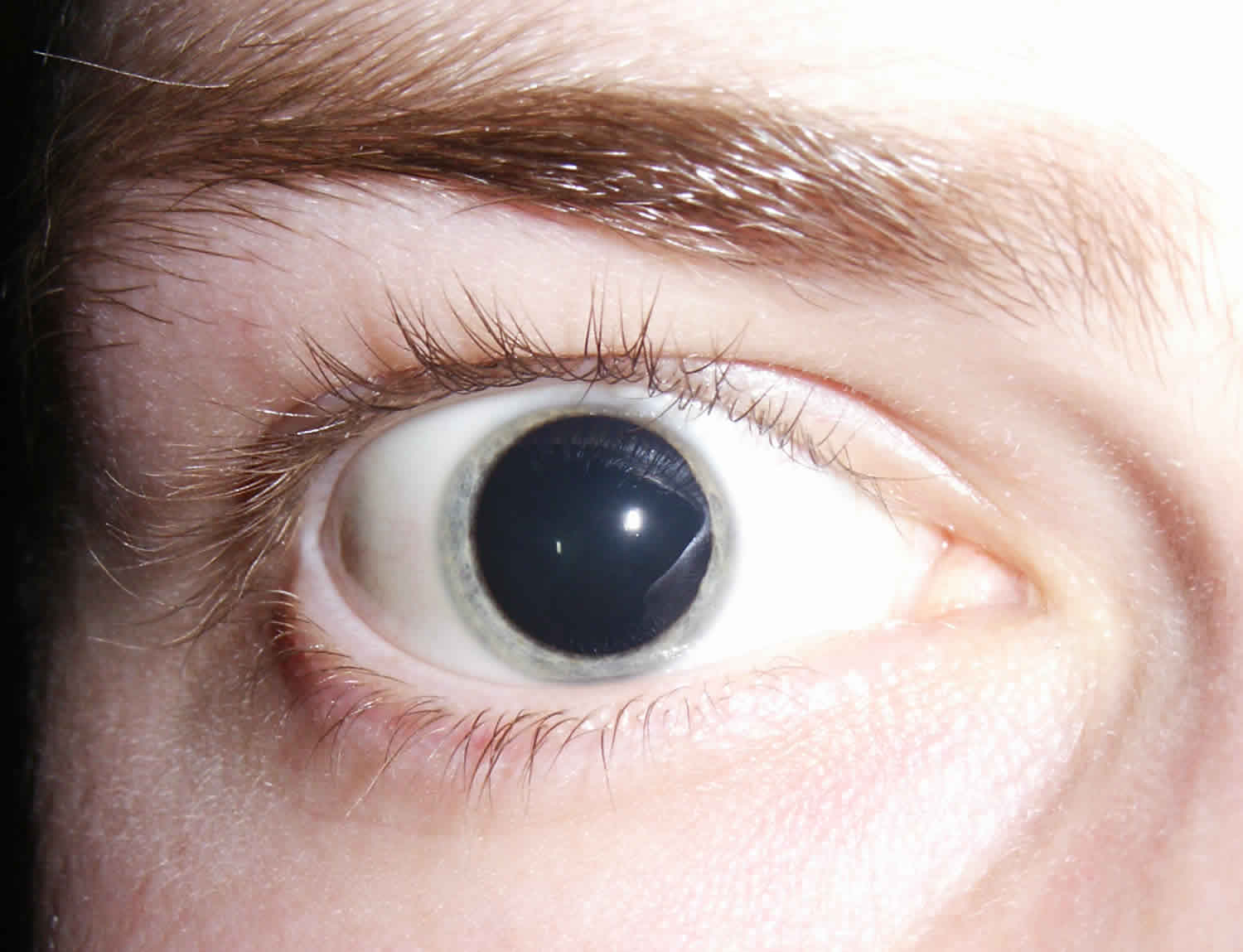
Could a simple glance reveal a hidden health concern, specifically within the window to your soul your pupils? Mydriasis, or the abnormal dilation of the pupils, serves as a critical indicator, often pointing to underlying medical conditions or external influences that demand immediate attention.
The iris, the colored part of your eye, houses a muscle that controls the pupil's size. This muscular dance allows the eye to adjust to varying light conditions. In dim environments, the pupil dilates to capture more light, while in bright settings, it constricts. However, when this natural process is disrupted, leading to mydriasis, it signifies a potential problem.
One of the primary associations of mydriasis is with angle-closure glaucoma, a serious eye condition. This is especially true in individuals with "narrow angles," referring to the restricted space between the iris and the cornea. When the pupil dilates, it can block the flow of fluid in the eye, leading to a dangerous buildup of pressure. This explains why mydriasis is a risk factor for angle closure glaucoma in certain individuals.
It's crucial to understand the difference between normal pupil dilation and mydriasis. Normal dilation occurs in response to low light or when focusing on distant objects. In contrast, mydriasis is characterized by dilated pupils that do not respond to light changes. This lack of reactivity is a key diagnostic clue. This is most commonly seen in those with "narrow angles," which refers to an unusually narrow angle between the outer edge of the iris and the cornea (the clear part of the eye that covers the front of the eye).
Several factors can trigger mydriasis. Medications, both prescription and over-the-counter, can affect pupil size. Recreational drugs, such as certain stimulants and hallucinogens, are well-known culprits. Additionally, injuries, particularly those affecting the eye or the brain, can lead to mydriasis. The opposite of mydriasis is pinpoint pupils, which indicate constriction.
The significance of pupil size extends beyond simple observation. The pressure that builds inside your brain after a head injury, stroke, or tumor can damage the iris muscles, disrupting their ability to regulate pupil size. The presence of a fixed, dilated pupil in an unconscious patient warrants immediate investigation, often raising suspicion of a serious intracranial issue, such as herniation due to an intracranial mass lesion. However, a fixed dilated pupil in an awake patient is not due to herniation.
Furthermore, mydriasis can arise from the use of dilating eye drops in eye health exams. These drops temporarily widen the pupils to allow the ophthalmologist to examine the back of the eye more thoroughly. This is a controlled, temporary effect and differs significantly from mydriasis caused by medical conditions or drugs.
Mydriasis, or a dilated pupil, often grabs attention due to its visibility, marking a change in eye appearance. But what conditions cause this? Several ocular disorders prevent pupil constriction, and diagnosing the underlying cause is a multi-step process. The causes are varied, spanning from medical conditions to medication side effects, each requiring specific treatment.
The determination of whether pharmacologic mydriasis, caused by topical agents, is present relies on a thorough examination. Certain eye drops, used for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, can cause dilation. A careful history of medication use, along with an eye exam and possibly specific testing, can help determine the cause.
| Mydriasis: Diagnostic and Clinical Overview | |
|---|---|
| Definition | Abnormal dilation of the pupil, exceeding a diameter of 5 mm, unresponsive to light stimuli or accommodation. |
| Causes |
|
| Symptoms |
|
| Diagnosis |
|
| Treatment |
|
| Complications |
|
| Reference | Mayo Clinic - Dilated pupils |
A case of traumatic mydriasis and accommodative dysfunction caused by a sweetgum ball ocular injury, with full resolution eight years after the inciting trauma, exemplifies the eye's remarkable capacity for recovery. It highlights the importance of long-term monitoring and the body's regenerative potential.
The opposite of mydriasis is miosis, or pinpoint pupils, where the pupils become abnormally constricted. Both conditions can be symptomatic of an underlying health issue and warrant medical evaluation. In German, the dilation of the pupil exceeding 5mm in diameter is referred to as "Als Mydriasis bezeichnet man die Weitstellung der Pupille ber einen Durchmesser von 5 mm hinaus."
The use of a comprehensive ophthalmology system like MYDRSI provides a structured method for diagnosis and management. It delivers standardized diagnostic protocols, personalized treatment plans, technological integration, and meticulous monitoring. In essence, MYDRSI helps practices manage their patient records, schedule appointments, and process insurance claims efficiently.
Mydriasis is when your pupils dilate unnaturally, not in response to darker environments. This unnatural dilation, and not in response to darker environments, is a key identifier and the source of many diagnostic questions.
The benefits of joining a program or accessing a digital platform are numerous and include free enrollment, course materials, and certifications. Further advantages are the ability to engage with other users and manage one's professional profile.
.jpg)